环境:服务器 Ubuntu12.04.5LTS + git(version 1.7.1) 客户端 Windows10 + git(version 2.8.4.windows.1)
① 安装 Git
Linux 做为服务器端系统,Windows 作为客户端系统,分别安装 Git
服务器端:
#sudo apt-get install git-core #ps -ef|grep "sshd" //查看是否配置了ssh #sudo apt-get install openssh-server openssh-client
安装完后,查看 Git 版本
[root@localhost ~]# git --versiongit version 1.7.1
客户端:
下载 ,地址:
安装完之后,可以使用 Git Bash 作为命令行客户端。
安装完之后,查看 Git 版本
$ git --versiongit version 2.8.4.windows.1
② 服务器端创建 git 用户,用来管理 Git 服务,并为 git 用户设置密码
[root@localhost home]# id gitid: git:无此用户[root@localhost home]# useradd git[root@localhost home]# passwd git
③ 服务器端创建 Git 仓库
设置 /home/data/git/gittest.git 为 Git 仓库
然后把 Git 仓库的 owner 修改为 git
[root@localhost home]# mkdir -p data/gittest.git[root@localhost home]# git init --bare data/gittest.git[root@localhost git]# chown -R git:git gittest.git/ [root@localhost git]# sudo chmod 755 /home/git/data
④ 客户端 clone 远程仓库
进入 Git Bash 命令行客户端,创建项目地址(设置在 d:/wamp64/www/gittest_gitbash)并进入,但首先要设置你的用户名称和e-mail地址。这是非常重要的,因为每次Git提交都会使用该信息。它被永远的嵌入到了你的提交中:
$ git config --global user.name "jiangxxxx" $ git config --global user.email "jiangxxx@163.com" $ cd gittest_gitbash
然后从 Linux Git 服务器上 clone 项目:
$ git clone git@192.168.71.130:/home/git/data/git.git $ git clone -b master git@192.168.71.130:/home/git/data/git.git/ ./ //克隆并切换到mater分支 $ git clone ssh://username@192.168.71.130/git
如果SSH用的不是默认的22端口,则需要使用以下的命令(假设SSH端口号是7700):
$ git clone ssh://git@192.168.56.101:7700/home/data/gittest.git
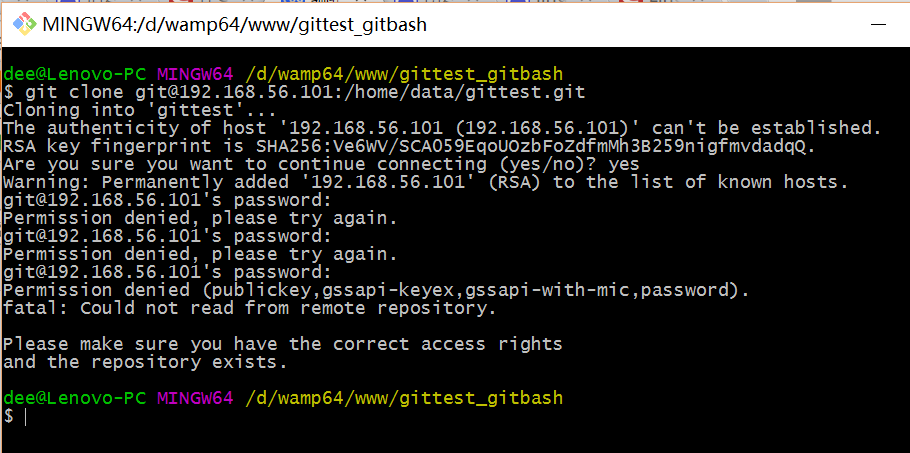
当第一次连接到目标 Git 服务器时会得到一个提示:
The authenticity of host '192.168.56.101 (192.168.56.101)' can't be established.RSA key fingerprint is SHA256:Ve6WV/SCA059EqoUOzbFoZdfmMh3B259nigfmvdadqQ.Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)?
选择 yes:
Warning: Permanently added '192.168.56.101' (RSA) to the list of known hosts.
此时 C:\Users\用户名\.ssh 下会多出一个文件 known_hosts,以后在这台电脑上再次连接目标 Git 服务器时不会再提示上面的语句。
后面提示要输入密码,可以采用 SSH 公钥来进行验证。
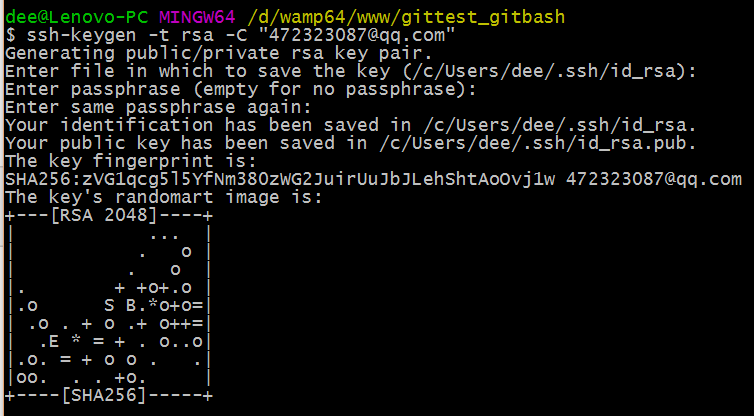
⑤ 客户端创建 SSH 公钥和私钥
$ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C "472323087@qq.com"
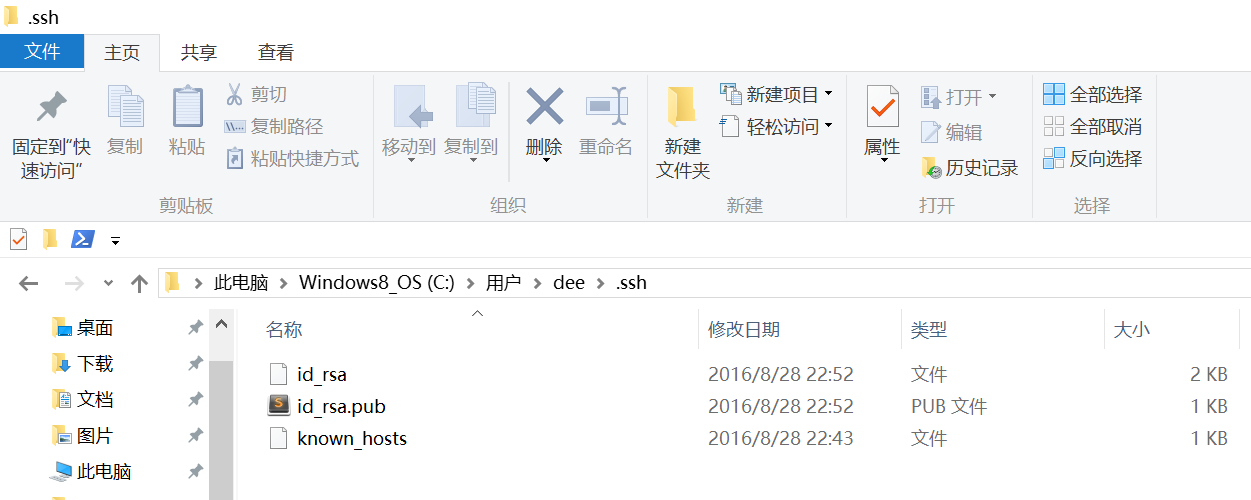
此时 C:\Users\用户名\.ssh 下会多出两个文件 id_rsa 和 id_rsa.pub
id_rsa 是私钥
id_rsa.pub 是公钥
⑥ 服务器端 Git 打开 RSA 认证
进入 /etc/ssh 目录,编辑 sshd_config,打开以下三个配置的注释:
RSAAuthentication yesPubkeyAuthentication yesAuthorizedKeysFile .ssh/authorized_keys
保存并重启 sshd 服务:
[root@localhost ssh]#sudo service ssh restart
由 AuthorizedKeysFile 得知公钥的存放路径是 .ssh/authorized_keys,实际上是 $Home/.ssh/authorized_keys,由于管理 Git 服务的用户是 git,所以实际存放公钥的路径是 /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys
在 /home/git/ 下创建目录 .ssh
[root@localhost git]# cd /home/git [root@localhost git]# mkdir .ssh [root@localhost git]# touch authorized_keys
[root@localhost git]# sudo scp ./id_rsa.pub 192.168.71.130:/home/git //客户端将公钥COPY到服务器
然后把 .ssh 文件夹的 owner 修改为 git
[root@localhost git]# chown -R git:git .ssh
[root@localhost git]# chmod 700 -R .ssh //注意.ssh权限,否则容易导致配置了ssh key,客户端clone时仍然需要密码
⑦ 将客户端公钥导入服务器端 /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys 文件
回到 Git Bash 下,导入文件:
$ ssh git@192.168.56.101 'cat >> .ssh/authorized_keys' < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub //客户端导入 $ cat /home/git/id_rsa.pub >> /home/git/.ssh/authorized_keys //或者服务器端直接导入
需要输入服务器端 git 用户的密码
回到服务器端,查看 .ssh 下是否存在 authorized_keys 文件:
[root@localhost git]# cd .ssh[root@localhost .ssh]# ll总用量 4-rw-rw-r--. 1 git git 398 8月 28 20:08 authorized_keys
可以查看一下是否是客户端生成的公钥。
重要:
修改 .ssh 目录的权限为 700
修改 .ssh/authorized_keys 文件的权限为 600
[root@localhost git]# chmod 700 .ssh[root@localhost git]# cd .ssh[root@localhost .ssh]# chmod 600 authorized_keys
⑧ 客户端再次 clone 远程仓库
$ git clone git@192.168.56.101:/home/data/git/gittest.git

查看客户端项目目录:
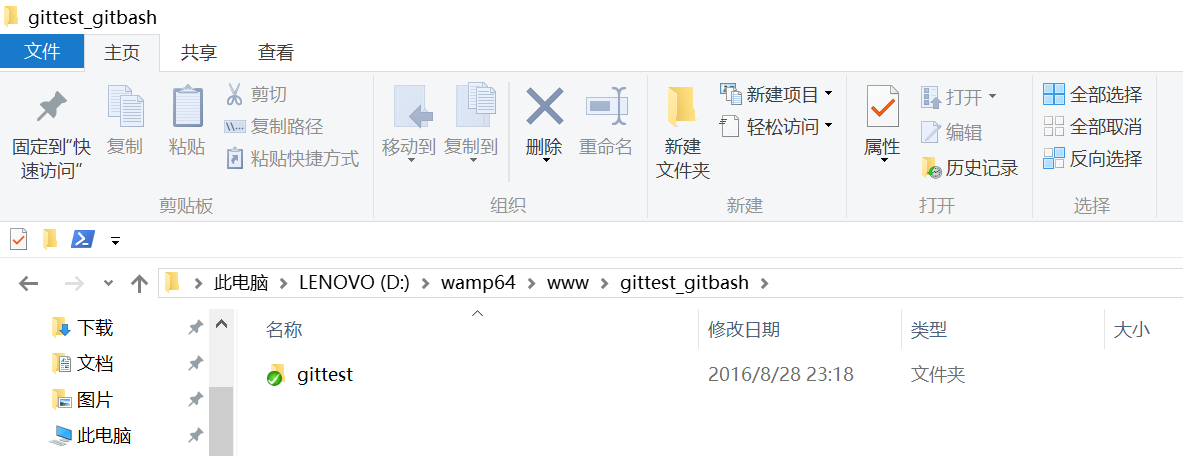
项目已经 clone 了。
也可以使用 tortoiseGit 客户端来管理项目:
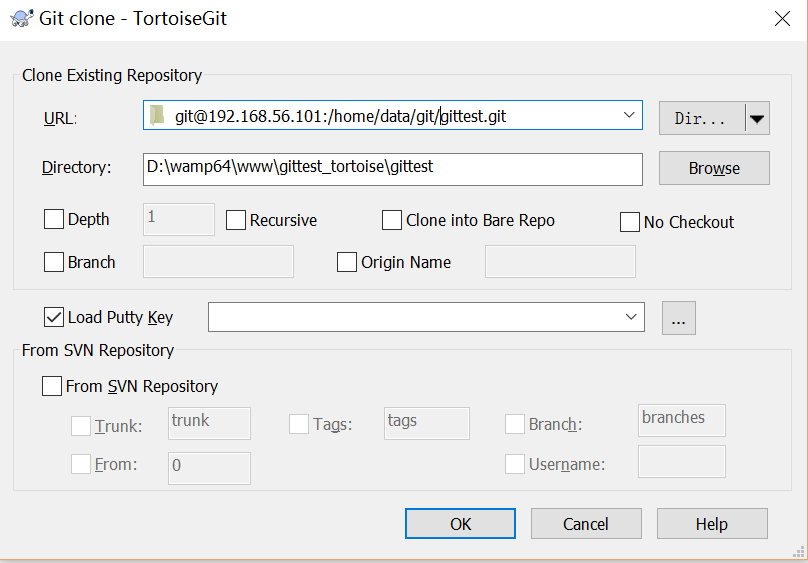
clone
⑨ 禁止 git 用户 ssh 登录服务器
之前在服务器端创建的 git 用户不允许 ssh 登录服务器
编辑 /etc/passwd
找到:
git:x:502:504::/home/git:/bin/bash
修改为
git:x:502:504::/home/git:/bin/git-shell
此时 git 用户可以正常通过 ssh 使用 git,但无法通过 ssh 登录系统。